Size exclusion chromatography, or SEC HPLC, is technique that sorts molecules by their size. This process allows scientists to study and describe the makeup of big molecules like polymers and proteins. It is used in many areas, like the pharmaceutical and biotech industries. It gives crucial details about the size and structure of these large molecules.12
Key Takeaways:
- SEC HPLC separates molecules based on their size or molecular weight.
- It is widely used for the analysis and characterization of polymers, proteins, and other macromolecules.
- SEC HPLC provides information about molecular weight distribution, aggregation, and degradation of samples.
- The technique is essential for quality control and R&D in industries working with large molecules.
- SEC HPLC has been in use since 1959 with ongoing developments for improved separations.
What is Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)?
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a technique for sorting out molecules by their size or weight. It’s also called gel filtration chromatography (GFC) or aqueous SEC. This separation method uses a column filled with porous beads. As the mixture flows through, smaller molecules enter the beads but larger ones go around them. This way, the molecules get separated by their size.3
Separation Technique Based on Molecular Size
SEC doesn’t sort molecules by how much they weigh. Instead, it looks at their size or volume. This is really useful for studying polymers, proteins, and bigger molecules. It helps researchers learn about these substances, telling them their weight distributions, and even if they’re sticking together or falling apart.
Applications of SEC HPLC in Polymer and Protein Analysis
SEC is used in many fields, including pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biotech. In the study of polymers, it helps figure out how big they are and if there are different sizes in the mix. It can also check if these polymers are tangled up or connected in different ways.2 In biotech, SEC comes in handy for understanding proteins, antibodies, and such. It shows scientists their sizes, if they’re grouping together, and how pure they are.3
| Fractionation Range | Application |
|---|---|
| Mr 100 to 7,000 | Peptides and small biomolecules |
| Mr 100,000 to 300,000 | Large proteins such as antibodies |
Chromatography resins for SEC come in different sizes. They’re made to work with a wide range of molecules. From tiny peptides to big antibodies, there’s a resin that can sort them all.2
Principles of SEC HPLC
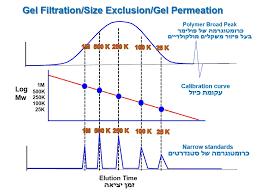
SEC HPLC separates molecules by their size or weight.4 It uses a special column. When the sample flows through, larger molecules can’t go through the columns. They come out first. But, smaller molecules can enter the column’s pores and stay longer, mixing up the sizes. This separation lets us see larger molecules go by first, followed by the smaller ones.4 We can even tell the size of each molecule by how fast or slow they move through the column.2
There are a few things that make the separation better in size exclusion chromatography. These include the size of the gel particles, how big the column is, and the speed the sample goes through.2 Using small gels makes it easier to see the differences. How big the pores are sets the limits for what it can separate.4 A longer column can help make the separation even better.4
Having too much empty space at the top of the column is bad because it makes the bands of molecules wider.4 The best separation happens when the sample moves through at just the right speed.4 We can find out how big unknown molecules are by using columns with known standards for comparison.4
| Resin Characteristics | Bio-Gel® P-10 | Bio-Gel® P-30 |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrated Bed Volume Mass | 7.5 ml/g4 | 90-180 µm4 |
| Typical Flow Rate | 15-20 cm/hr4 | 9 ml/g4 |
| Molecular Weight Fractionation Range | 1,500-20,0004 | 2,400-40,0004 |
The resins in SEC can sort different sizes of molecules. Some are good for finding small peptides. Others work well for big proteins like antibodies.2
Instrumentation for SEC HPLC
The SEC HPLC setup includes important tools like a solvent system, an autosampler, a column heater, a detector, and data software.5 These parts team up to sort and measure big molecules, for example, plastics and proteins by their size.
HPLC System Components
The solvent system keeps the liquid moving consistently, needed for good separation. An autosampler adds samples with precision. The column heater keeps things at the right temperature for best results.6 A UV-Vis or refractive index detector checks the sample as it flows out of the column, making graphs we can read.
SEC Columns and Packing Materials
In SEC HPLC, the main items are the columns and what’s inside them. Columns are filled with tiny, porous beads. These might be cross-linked polystyrene or polymethacrylate. They have special holes that let big molecules get caught depending on their size.6 Choosing the correct column and beads is critical. It relies on things like what sizes of molecules you’re checking, your sample, and how clear you need the results to be.
| SEC Column Packing Material | Molecular Weight Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-linked polystyrene | 100 – 10,000,000 Da | Polymer analysis, protein analysis |
| Polymethacrylate | 100 – 1,000,000 Da | Protein analysis, antibody characterization |
| Dextran | 100 – 2,000,000 Da | Carbohydrate analysis, protein analysis |
Sample Preparation for SEC HPLC Analysis
Getting the sec hplc sample preparation right is key for a successful SEC HPLC look-over. It’s important to put your samples in the right solvent. This prevents any mix-ups with the substance the samples are sitting on.7 You might spin your samples at high speeds to get rid of certain parts, like tiny leftover bits or proteins that stick to filters. Plus, how you spin them differs based on what’s in your sample.7
Dissolving and Filtering Samples
Another must-do is to filter your samples. This takes out anything solid that might block the column.7 To filter, you can use special membranes made of cellulose acetate or PVDF. You should pick the filter size depending on how big the chromatography beads are. This is to make sure it cleans up well.
Concentration and Injection Volume
It’s also crucial to get the sample concentration and injection volume just right. This makes sure you see what you’re looking for clearly.2 When working with biomolecules, you need a careful touch. Sample sizes should be just a small part of the total column volume, and you should apply them slowly through long columns. This is to avoid putting too much or too little into the system.
Putting too much on the column can mess up the results. It might not show the true weight of the molecules. But, if you put too little, the signal you get back might not be clear. So, a balance is needed.
Optimizing SEC HPLC Conditions
To get precise and repeatable results in SEC HPLC, we need to optimize some key things. It’s vital to pick the right mobile phase and fine-tune the flow rate and temperature.
Choosing the Right Mobile Phase
In SEC HPLC, the mobile phase must work well with the sample and column. It can be made of aqueous buffers, organic solvents, or a mix. The choice depends on what you’re testing and why.8 The mix’s ionic strength, pH level, and buffer type can change how well you see different peaks in your results.8
Flow Rate and Temperature
The speed and heat of the mobile phase really matter in SEC HPLC.8 A faster flow can cut down testing time but might blur the peaks. Also, the heat can change how thick the mobile phase is and how it moves through the column.8 For instance, using a smaller column can mean using less sample, like 33% less. And, the flow needed is different for small and large molecules.8 Big changes in temperature, like more than 10 degrees, can mess with how well the mobile phase works, the column’s pressure, and how samples move in the column.8
By choosing the right mobile phase and tweaking the flow and temperature, scientists can boost how well SEC HPLC works. This leads to better, more trustworthy findings for [sec hplc mobile phase], [flow rate optimization], [temperature effects], and [separation efficiency].
Data Analysis and Interpretation of SEC HPLC Results
Understanding SEC HPLC data is key to gaining meaningful insights. It shows things like peak retention times and widths. Also, it highlights peak areas, aiding in knowing the sample’s makeup and size distribution.5 By matching these times with standards of known weights, we find the sample’s weight spread. This helps find out numbers like average molecular weight and size variation. These numbers tell us how consistent the sample’s properties are.
Chromatogram Features
Peak times, widths, and areas are key in knowing what’s in the sample and how big the molecules are.9 We use these clues to check for purity and how the molecules stick together. This is vital in studying medicine molecules and antibodies.
Calculating Molecular Weight Distributions
Comparing peak times with standards lets us figure out the molecules’ sizes in the sample.5 We then find out key numbers like average and typical weight. This helps understand the structure of polymers and proteins. It is important for checking their quality and making better products.
Applications of SEC HPLC
SEC HPLC is used in many areas, from polymer science to biotechnology. This powerful tool helps analyze the structure of big molecules. It is key in studying the properties and makeup of both synthetic and natural large molecules.
Polymer Characterization
For polymers, SEC HPLC is critical. It checks the spread of molecular sizes, finds low and high weight parts, and looks for branching. This data is vital for knowing how polymers behave in things like plastics and coatings. It affects their strength and flexibility.
Protein and Antibody Analysis
In biotech, SEC HPLC plays a big role in analyzing proteins and antibodies. It tells us about their size, if they stick together, and if they’re pure. This really matters in making sure medicines are good quality.1011 It can even check for protein lumps, which health officials worry about because they might cause bad reactions.10 New types of SEC, like SE-UHPLC, can see tiny changes in proteins better. This is very important for studying unique parts of certain drugs.10
Moreover, SEC remains very important for sorting and describing proteins. With tools that work really fast and with great detail, it’s become even more useful.11 Thanks to new materials in SEC, such as extra-tiny particles, it can do more than ever before. It can separate even very similar proteins better, helping in a wide range of research and product testing.11
Advantages and Limitations of SEC
Size exclusion chromatography, or SEC, is great at sorting molecules by their molecular size2. It’s easy to get samples ready, too2. SEC HPLC tells us a lot about molecular weight distribution and how the samples are put together. And it does it all without needing a lot of work upfront. This is why SEC HPLC is key in areas like making plastics, studying proteins, and in biotech.
SEC HPLC does have its downsides, though. Samples might stick to or react with the column’s material. This could mess up the results12. Plus, to figure out the sizes of the molecules, we need to use special calibration standards. How well this works depends on picking and preparing these standards carefully12. Getting exact and repeatable results also means tweaking the details of the tests. Think about the liquid used, how fast it flows, and how hot or cold it is.
In the end, SEC HPLC’s strong points and its challenges balance each other out. It’s effective in separating molecules by size and needs straightforward sample prep. But, you have to be careful when setting up the tests and watch out for sample-column interactions. Knowing both the good and the tough parts of this technique helps scientists and analysts get the most out of it. They can use SEC HPLC to dig deep into the makeup and design of big molecules like plastics and proteins.
Source Links
- https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/primers/public/5991-3651EN_LR.pdf
- https://www.cytivalifesciences.com/en/us/solutions/protein-research/knowledge-center/protein-purification-methods/size-exclusion-chromatography
- https://phenomenex.blog/2020/09/24/size-exclusion-chromatography/
- https://www.bio-rad.com/en-us/applications-technologies/introduction-size-exclusion-chromatography?ID=LUSMV015
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3556795/
- https://www.ssi.shimadzu.com/service-support/technical-support/analysis-basics/basic/55/55intro.html
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/protocol/protein-biology/protein-purification/sample-preparation
- https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/optimizing-sec-biologics-analysis-0
- https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/size-exclusion-chromatography-analysis-complex-and-novel-biotherapeutic-products-1
- https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/size-exclusion-chromatography-analysis-complex-and-novel-biotherapeutic-products
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/materials-science/size-exclusion-chromatography
- https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/the-benefits-of-multi-angle-light-scattering-for-size-exclusion-chromatography