Bovine gelatin is a natural protein derived from the collagen of cows, widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Known for its gelling, stabilizing, and thickening properties, it plays a crucial role in the production of gummy candies, marshmallows, yogurts, and pharmaceutical capsules. Beyond its functional uses, bovine gelatin is also prized for its health benefits, particularly in joint support, skin elasticity, and gut health.
With growing interest in collagen-based supplements, many people are turning to bovine gelatin as a natural source of amino acids that promote overall well-being. But what exactly is bovine gelatin, and how does it compare to other types of gelatin?
In this article, we’ll explore its origins, benefits, uses, and safety considerations, helping you understand why it has become such a valuable ingredient in health and nutrition.
What Is Bovine Gelatin?
Bovine gelatin is a protein-based substance derived from the collagen of cows, primarily extracted from their skin, bones, and connective tissues. It is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties.
How Is Bovine Gelatin Made?
The production of bovine gelatin involves several steps:
- Collagen Extraction – Raw materials (cow hides and bones) are cleaned and treated to extract collagen.
- Hydrolysis Process – The collagen is broken down using acid or alkaline treatments.
- Purification & Filtration – The extracted gelatin is purified to remove impurities.
- Drying & Powder Formation – The final product is dried and processed into powder or sheets.
Key Properties of Bovine Gelatin
- Rich in Collagen – Contains Type I & III collagen, which is essential for skin, joints, and connective tissues.
- Gelling Ability – When dissolved in hot water and cooled, it forms a gel-like texture, making it ideal for food and pharmaceuticals.
- High in Amino Acids – Provides glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which support skin elasticity and gut health.
- Neutral in Taste & Odor – Suitable for various food applications without altering flavor.
Bovine Gelatin vs. Other Gelatin Types
- Bovine vs. Porcine Gelatin – Bovine gelatin is sourced from cows, while porcine gelatin comes from pigs. Some people prefer bovine gelatin for religious or dietary reasons (Halal & Kosher options).
- Bovine vs. Fish Gelatin – Fish gelatin is an alternative for those who avoid mammal-based gelatin, but it has different gelling properties.
- Bovine vs. Plant-Based Alternatives – Unlike agar-agar or pectin, which are derived from plants, bovine gelatin provides protein and collagen benefits.
Bovine gelatin is more than just a food ingredient—it is a functional protein with numerous health benefits, making it a valuable addition to both dietary supplements and skincare products.
Nutritional Composition of Bovine Gelatin
Bovine gelatin is a protein-rich substance, offering a unique nutritional profile that makes it beneficial for skin health, joint support, and digestion. Unlike other protein sources, gelatin is almost entirely made of amino acids, particularly those that support connective tissue repair and gut health.
Macronutrient Breakdown (Per 100g of Bovine Gelatin Powder)
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 350 kcal |
| Protein | 85-90g |
| Carbohydrates | 0g |
| Fats | 0g |
| Water | 8-10g |
🔹 Key Takeaway: Bovine gelatin is high in protein, zero in fat and carbs, making it a great low-calorie, high-protein supplement for various diets.
Amino Acid Profile of Bovine Gelatin
Bovine gelatin contains 18 amino acids, with high levels of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which are essential for collagen synthesis.
| Amino Acid | Function in the Body |
|---|---|
| Glycine (~27%) | Supports gut health, sleep, and anti-inflammatory functions |
| Proline (~16%) | Helps in skin regeneration and wound healing |
| Hydroxyproline (~14%) | Strengthens connective tissues and bones |
| Glutamic Acid (~10%) | Supports brain function and metabolism |
| Alanine (~9%) | Provides energy and enhances muscle performance |
Does Bovine Gelatin Contain Vitamins & Minerals?
While bovine gelatin is rich in proteins and amino acids, it contains minimal vitamins and minerals. However, it enhances nutrient absorption when combined with vitamin C and minerals like zinc, which are essential for collagen production in the body.
Why Is Bovine Gelatin a Great Protein Alternative?
✔ Easy to digest – Unlike meat-based proteins, gelatin is gentle on the stomach.
✔ Supports gut lining – Helps improve digestive health and reduce leaky gut symptoms.
✔ No fat or sugar – Ideal for low-carb, keto, and high-protein diets.
Bovine gelatin is not just a protein supplement—it’s a functional food with numerous health benefits, making it a valuable ingredient in nutrition, skincare, and joint support.
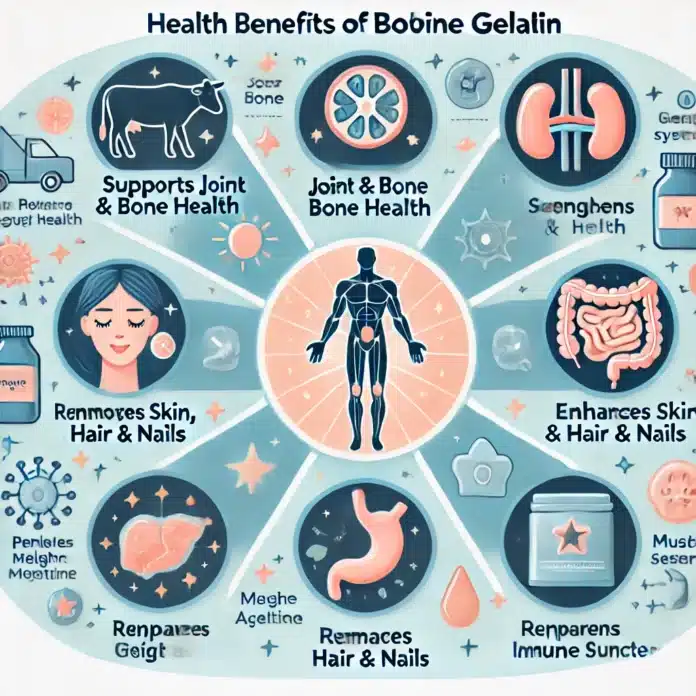
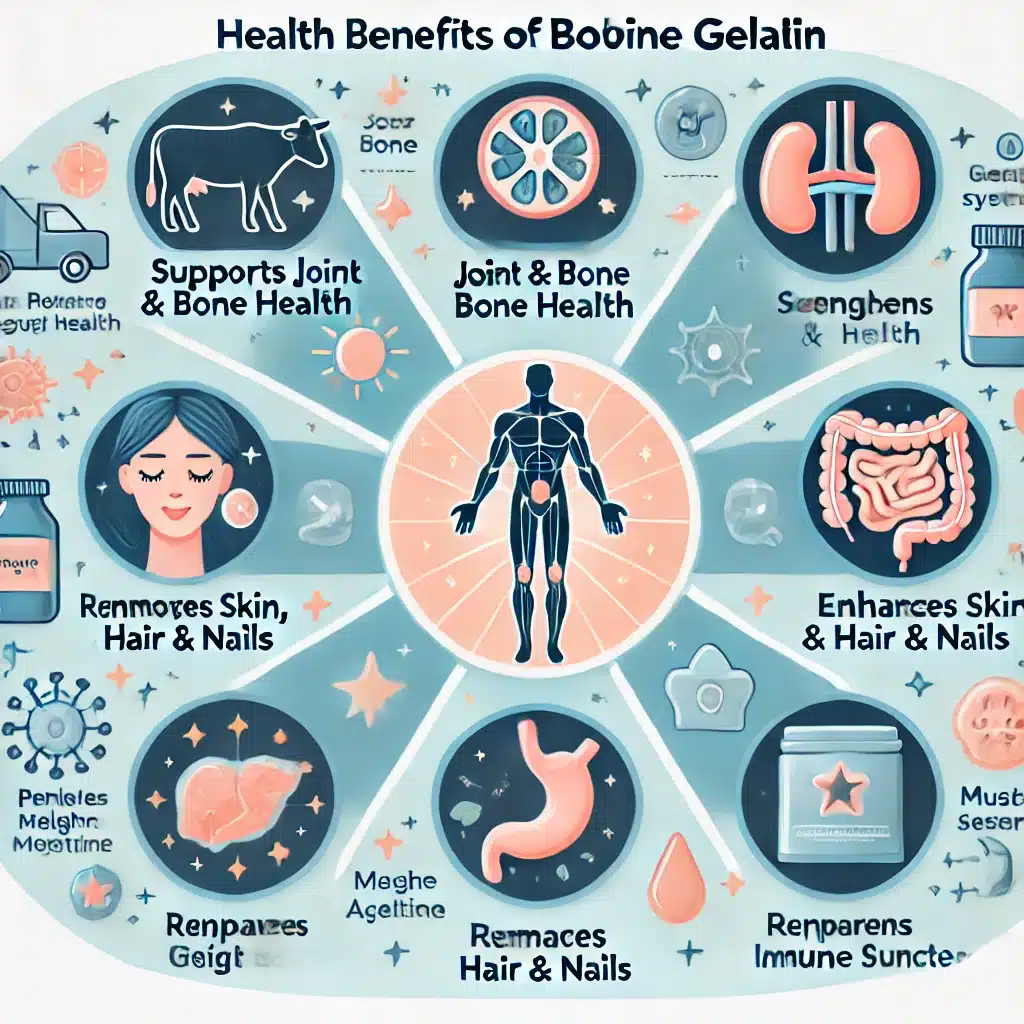
Health Benefits of Bovine Gelatin
Bovine gelatin is more than just a culinary ingredient—it’s a functional food with a wide range of health benefits. Rich in collagen-building amino acids, it plays a crucial role in joint health, digestion, skin rejuvenation, and overall well-being.
🔹 1. Supports Joint & Bone Health 🦴
- Contains collagen-building amino acids (glycine, proline, hydroxyproline) that strengthen cartilage and bones.
- Helps reduce joint pain and stiffness, making it beneficial for people with arthritis and osteoporosis.
- Improves joint flexibility and recovery for athletes and active individuals.
✅ How to Use: Regular consumption of bovine gelatin may help reduce the risk of joint degeneration.
🔹 2. Promotes Healthy Skin, Hair & Nails 💆♀️
- Boosts collagen production, improving skin elasticity, hydration, and reducing wrinkles.
- Strengthens hair and nails, preventing breakage and promoting faster growth.
- Helps in skin regeneration and wound healing.
✅ How to Use: Drinking gelatin-based collagen drinks or adding it to smoothies can improve skin health naturally.
🔹 3. Aids Digestion & Gut Health 🏥
- Helps repair the gut lining, reducing leaky gut syndrome and digestive disorders.
- Supports healthy digestion by promoting the production of gastric juices and enzymes.
- Soothes the intestinal lining, which is beneficial for IBS, acid reflux, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
✅ How to Use: Bone broth, gelatin desserts, or supplements can support a healthy gut microbiome.
🔹 4. Enhances Sleep & Brain Function 🧠💤
- Glycine (27%) in gelatin promotes deep, restful sleep and reduces stress and anxiety.
- Improves memory, focus, and cognitive function by supporting neurotransmitter balance.
- May help reduce brain fog and enhance mood.
✅ How to Use: Drinking a cup of warm gelatin-infused tea before bed can improve sleep quality.
🔹 5. Supports Weight Loss & Muscle Recovery 💪
- High in protein (85-90%) and low in calories, making it ideal for weight management.
- Increases satiety, reducing cravings and helping with appetite control.
- Assists in muscle recovery and growth, especially post-workout.
✅ How to Use: Add gelatin powder to protein shakes, smoothies, or soups for muscle repair and weight control.
🔹 6. Strengthens the Immune System 🛡️
- Provides essential amino acids that support immune function and anti-inflammatory responses.
- Helps the body recover from illnesses faster by reducing inflammation.
✅ How to Use: Consuming gelatin regularly can contribute to a stronger immune defense.
Final Thoughts
Bovine gelatin is a nutrient-dense superfood that supports joint, skin, gut, and brain health while also aiding in weight loss and immunity. Incorporating it into your diet through soups, broths, supplements, or homemade desserts is an easy way to reap its benefits.
5. Uses of Bovine Gelatin
Bovine gelatin has a wide range of applications across different industries, making it a versatile ingredient with numerous benefits. Below are some of its primary uses:
Food Industry
Bovine gelatin is commonly used in the food industry due to its ability to thicken, stabilize, and add texture to various products. Here are some common food applications:
- Gummies: Gelatin is a key ingredient in gummy candies, offering their chewy texture.
- Marshmallows: Bovine gelatin gives marshmallows their soft, airy consistency.
- Yogurt & Jell-O: It helps thicken and stabilize these products, making them smoother and creamier.
- Desserts: It is often used in desserts like panna cotta, mousses, and fruit gels to improve texture and consistency.
Gelatin serves as an excellent thickener and stabilizer in these food products, making them more appealing to consumers.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical world, bovine gelatin is most commonly used in the production of capsules and softgels. Gelatin is used as a coating for tablets and capsules, ensuring they are easy to swallow and protected from the environment. Additionally, it is found in wound healing formulations due to its collagen content, which promotes tissue regeneration and healing.
Cosmetic Industry
Gelatin is also an important ingredient in the cosmetic industry, where it is used in a variety of products aimed at improving skin and hair health:
- Skincare: Bovine gelatin is included in moisturizers, serums, and masks, thanks to its collagen-promoting properties that help reduce the appearance of wrinkles and improve skin elasticity.
- Hair masks: It is found in hair care products designed to strengthen and restore hair by promoting keratin production.
- Beauty supplements: Gelatin is often included in beauty supplements that target healthier skin, hair, and nails.
Medical & Dietary Uses
Bovine gelatin is also a popular choice in the form of dietary supplements, particularly for individuals looking to enhance joint health, improve skin elasticity, and support gut health. Common uses include:
- Bone broth supplements: Gelatin derived from bovine bones is a key ingredient in bone broth supplements, known for their ability to support joint and digestive health.
- Hydrolyzed collagen peptides: Bovine gelatin is hydrolyzed into collagen peptides for easier digestion, commonly used to support healthy aging, joint function, and skin regeneration.
6. Bovine Gelatin vs. Other Gelatins
When choosing gelatin, it’s important to consider various types, as each has distinct properties and benefits. Below is a comparison of bovine gelatin with other common types of gelatins:
Bovine vs. Porcine Gelatin – Dietary & Religious Considerations
Bovine gelatin, derived from cows, is often compared to porcine gelatin, which comes from pigs. One of the main differences lies in dietary and religious preferences.
- Halal and Kosher Considerations:
- Bovine gelatin can be considered Halal or Kosher if the cow is slaughtered according to religious guidelines. However, porcine gelatin is generally not Halal or Kosher due to the religious restrictions on pork.
- People who observe Halal or Kosher dietary laws may prefer bovine gelatin, particularly if they know it is sourced from animals that adhere to those standards.
- Health Considerations:
Both bovine and porcine gelatin offer similar nutritional benefits, as they are both rich in amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. The difference largely comes down to individual dietary restrictions.
Bovine vs. Fish Gelatin – Differences in Amino Acid Profile & Use in Skincare
Fish gelatin is another alternative to bovine gelatin, often derived from the skin and bones of fish. Here’s how bovine gelatin compares to fish gelatin:
- Amino Acid Profile:
- Both bovine and fish gelatin are rich in collagen, but fish gelatin tends to have a slightly different amino acid composition, particularly in the glycine and proline content, which might offer specific benefits for different health concerns.
- Fish gelatin may be preferred by people seeking a marine collagen source, as it is thought to have slightly higher bioavailability (the body’s ability to absorb and use the gelatin).
- Use in Skincare:
- Fish gelatin is commonly found in skincare products aimed at improving skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles. It is especially favored for its marine collagen benefits, which are believed to be more effective in skin regeneration.
- While bovine gelatin also promotes collagen synthesis and skin elasticity, fish gelatin is often preferred in products marketed for beauty and anti-aging due to its higher absorption rates.
Bovine vs. Plant-Based Gelatin (Agar-Agar, Pectin) – Vegan Alternatives
For those who avoid animal-derived products, plant-based gelatins like agar-agar and pectin are popular alternatives. Here’s how they compare to bovine gelatin:
- Agar-Agar:
- Derived from red algae, agar-agar is a vegan alternative to gelatin that behaves similarly in cooking and food preparation. It is often used as a thickening agent in desserts, jellies, and vegan gummies.
- Agar-agar sets at a higher temperature than gelatin and has a firmer texture, which makes it ideal for certain applications but might not provide the same texture or mouthfeel as bovine gelatin.
- Pectin:
- Pectin is another plant-based option found in fruits, commonly used for making jams, jellies, and other confections. While it is plant-derived, pectin has a different setting mechanism and is not a direct substitute for gelatin in all recipes. It is typically used in fruit-based products and lacks the collagen-building benefits of bovine gelatin.
Plant-based gelatins are a great alternative for vegans or individuals with dietary restrictions, but they lack some of the health benefits of bovine gelatin, such as joint support and collagen production.
Is Bovine Gelatin Safe?
Bovine gelatin is generally considered safe for most people when consumed in appropriate amounts, but, as with any dietary supplement or ingredient, there are some important safety considerations to keep in mind. Below, we discuss common concerns related to allergies, sourcing, and regulations:
Allergies and Safety Concerns
While bovine gelatin is not a common allergen, some individuals may experience allergic reactions, especially if they have sensitivities to beef products or have other food allergies. It is important to note that reactions to gelatin are rare, but symptoms may include rashes, hives, or digestive discomfort.
- If you are allergic to beef or have sensitivities to certain animal products, you should consult with a healthcare provider before consuming bovine gelatin.
- Cross-contamination: In some cases, gelatin products may be processed in facilities that handle other allergens (such as dairy or gluten), so always check product labels for any potential cross-contamination risks.
Sourcing and Quality of Gelatin
The quality and safety of bovine gelatin are directly influenced by its sourcing and the conditions under which the animals are raised. High-quality gelatin is typically sourced from grass-fed, organic cattle, which ensures that the gelatin is free from harmful chemicals, antibiotics, and hormones.
- Grass-fed gelatin: Gelatin made from grass-fed cows is considered to be of higher quality because it typically contains more beneficial nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
- Organic gelatin: Organic gelatin is made from cattle raised without synthetic hormones, antibiotics, or genetically modified feed, making it a better choice for those seeking a cleaner, more natural product.
- Always look for gelatin products that are clearly labeled grass-fed and organic to ensure they meet high-quality standards.
Regulations: FDA & EFSA Guidelines on Gelatin Purity
Bovine gelatin is regulated by authorities such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States and the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) in Europe, ensuring that it meets safety and purity standards.
- The FDA has established guidelines for the safety of food ingredients like gelatin, ensuring that it is free from contaminants and meets purity standards. All gelatin sold in the U.S. must be tested for safety and purity before being approved for use in food and supplements.
- The EFSA similarly regulates gelatin in Europe, focusing on its use in food and dietary supplements. It sets strict standards for gelatin purity, ensuring that the product is free from harmful chemicals and contaminants.
- Gelatin certifications: Both the FDA and EFSA require manufacturers to provide documentation on the sourcing and purity of gelatin, ensuring that it is safe for human consumption. Look for certifications like GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) and ISO to ensure that the gelatin meets these regulatory standards.
How to Use Bovine Gelatin?
Bovine gelatin is a versatile ingredient that can be easily incorporated into your daily routine. Whether you’re looking to boost your joint health, improve skin elasticity, or simply enjoy the texture it adds to your food, here’s how you can use it effectively:
Daily Dosage Recommendations for Supplements
When it comes to supplementation, the ideal daily dosage of bovine gelatin (or hydrolyzed collagen) can vary depending on the specific health goals you’re targeting. However, a common dosage range is:
- For joint health: 10–15 grams per day is often recommended to support cartilage repair and reduce inflammation.
- For skin health: 5–10 grams per day can help improve skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles.
- For gut health: 10 grams per day can assist with digestion and help support a healthy gut lining, particularly in cases of leaky gut syndrome.
It’s best to start with a lower dosage and gradually increase based on your body’s response. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Recipes: How to Make Homemade Gelatin Gummies
Homemade gelatin gummies are a delicious and easy way to incorporate bovine gelatin into your diet. Here’s a simple recipe to try:
Ingredients:
- 1 cup fruit juice (fresh or store-bought, preferably without added sugar)
- 3 tablespoons bovine gelatin powder
- 1–2 tablespoons honey (optional, for sweetness)
Instructions:
- Pour the fruit juice into a small saucepan and heat gently over medium heat.
- Once the juice is warm (but not boiling), add the gelatin powder. Stir continuously to dissolve the gelatin completely.
- Add honey for sweetness, if desired, and stir until well combined.
- Pour the mixture into silicone molds or a lined baking dish.
- Refrigerate for at least 2–3 hours or until the gummies have set.
- Remove from molds and enjoy your homemade gelatin gummies!
These gummies are a fun and tasty way to get your daily dose of gelatin, especially for kids or adults who might struggle to consume it in other forms.
Best Ways to Incorporate It Into Your Diet (Smoothies, Soups, Desserts)
Bovine gelatin can be added to a variety of dishes to enhance texture, improve nutritional value, and support your health goals. Here are some easy ways to incorporate gelatin into your daily meals:
- Smoothies: Simply add 1–2 tablespoons of gelatin to your smoothie, and blend it with your usual ingredients. The gelatin will thicken the smoothie and provide a collagen boost for skin and joint health.
- Soups and Broths: Bone broth is one of the best ways to consume gelatin, as it is rich in collagen. You can also dissolve gelatin powder into hot soups and stews to enhance their richness and nutritional profile.
- Desserts: Add gelatin to homemade desserts like panna cotta, mousse, or custards to improve texture and add health benefits. It also works great in fruit gels or no-bake cheesecakes.
Gelatin can be easily mixed into hot or cold dishes, making it a versatile and simple addition to your meals.
Where to Buy Bovine Gelatin?
Finding high-quality bovine gelatin is essential for ensuring you’re getting the full benefits of this nutrient-rich product. Below are some top brands and where you can find the best gelatin powder to support your health:
Top Brands
When it comes to quality, certain brands stand out for their commitment to purity, sourcing, and customer satisfaction. Some of the best-known and trusted brands include:
- Great Lakes Gelatin: Known for its premium hydrolyzed collagen products, Great Lakes Gelatin offers a range of gelatin options, including powdered and flavored versions. Their gelatin is derived from grass-fed, pasture-raised cows, ensuring a high-quality product that is non-GMO and free from additives.
- Vital Proteins: Specializing in collagen peptides, Vital Proteins offers hydrolyzed bovine gelatin that is highly bioavailable. Their gelatin is sourced from grass-fed cattle and is available in both powder and capsule forms. Vital Proteins is particularly known for its focus on skin and joint health.
- Now Foods: Offering a variety of collagen supplements, Now Foods provides high-quality bovine gelatin powder that is non-GMO and gluten-free. Their gelatin is a popular choice for those seeking a cost-effective and reliable option for daily supplementation.
Where to Find High-Quality, Hydrolyzed Gelatin Powder
You can find high-quality products at several trusted retailers, both online and in-store:
- Amazon: Amazon offers a wide selection of bovine gelatin powders, including products from brands like Great Lakes Gelatin, Vital Proteins, and Now Foods. Reviews from other users can help guide your purchasing decision, ensuring that you choose the right product for your needs.
- Health Food Stores: Retailers like Whole Foods Market and Trader Joe’s often carry high-quality gelatin products, including hydrolyzed options. Look for gelatin that is labeled as grass-fed and organic to ensure quality.
- Specialty Supplement Stores: Websites like iHerb and Swanson Health offer a wide range of bovine gelatin supplements. These stores often provide detailed product descriptions and customer reviews, making it easier to compare different options.
- Direct from Manufacturers: Purchasing directly from the brand’s website (e.g., Great Lakes Gelatin, Vital Proteins) can often give you access to the latest product releases, discounts, and bundles. This can be a great option for those who want to try multiple products or stock up on their favorite brand.
When purchasing it, always check the product labels for key factors like sourcing, grass-fed status, and hydrolyzed formulation to ensure you are getting the highest quality product.
Conclusion
Bovine gelatin is a versatile and beneficial ingredient, offering a wide range of health benefits, from supporting joint health to improving skin elasticity. Whether you’re using it in supplements, recipes, or as a food ingredient, incorporating gelatin into your routine can help enhance overall well-being. With high-quality options available from trusted brands, it’s easy to find the right product for your needs. If you haven’t already, consider adding bovine gelatin to your daily regimen and enjoy its numerous health benefits!